When it comes to heart health, accurate diagnosis is crucial. Two key imaging techniques – cardiac CT scan vs angiogram – are often compared for the detailed views they provide of your heart’s structure and function.
CT scans offer non-invasive 3D imaging, while angiograms provide real-time blood flow visualization. But which one is right for you?
This guide compares cardiac CT scan vs angiogram, detailing their processes, benefits, and potential risks. We’ll explore scenarios where each test excels so you can navigate your cardiac care journey with confidence.
| Curious about other heart tests? Check out our comprehensive guide to 13 common heart tests and when you need them. |
Understanding Cardiac CT Scan (CT Angiography)
A Cardiac CT Scan, or CT Angiography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the heart and blood vessels.This advanced form of Cardiac CT Imaging provides clear and precise pictures of the coronary arteries, allowing doctors to assess blood flow and detect blockages or abnormalities.
Cardiac CT scan procedure involves several steps:
- Preparation: We recommend fasting for a few hours prior to the scan. Your healthcare provider might also instruct you to avoid specific medications or substances that could affect the results.
- Contrast Dye Injection: A contrast dye is injected into a vein in your arm to enhance the visibility of blood vessels and heart chambers in the scan images.
- Scanning: You’ll lie on a table that slides into the CT scanner. The scanner – a large, doughnut-shaped machine – will take multiple X-ray images of your heart from various angles. It’s essential to remain still and hold your breath briefly (5 to 10 seconds) while the machine captures multiple images.
- Post-Procedure: After the scan, you can typically resume normal activities almost immediately. A radiologist analyzes the images, interprets the results, and discusses them with your doctor.
Uses of Cardiac CT Scans:
- Assessing Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Detects blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries.
- Evaluating Heart Valves: Provides detailed images of the heart valves to identify any issues.
- Detecting Congenital Heart Defects: Identifies structural problems present from birth.
The primary advantage of a Cardiac CT Scan is its non-invasive nature. It provides detailed images quickly for efficient diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions.
Understanding Angiogram
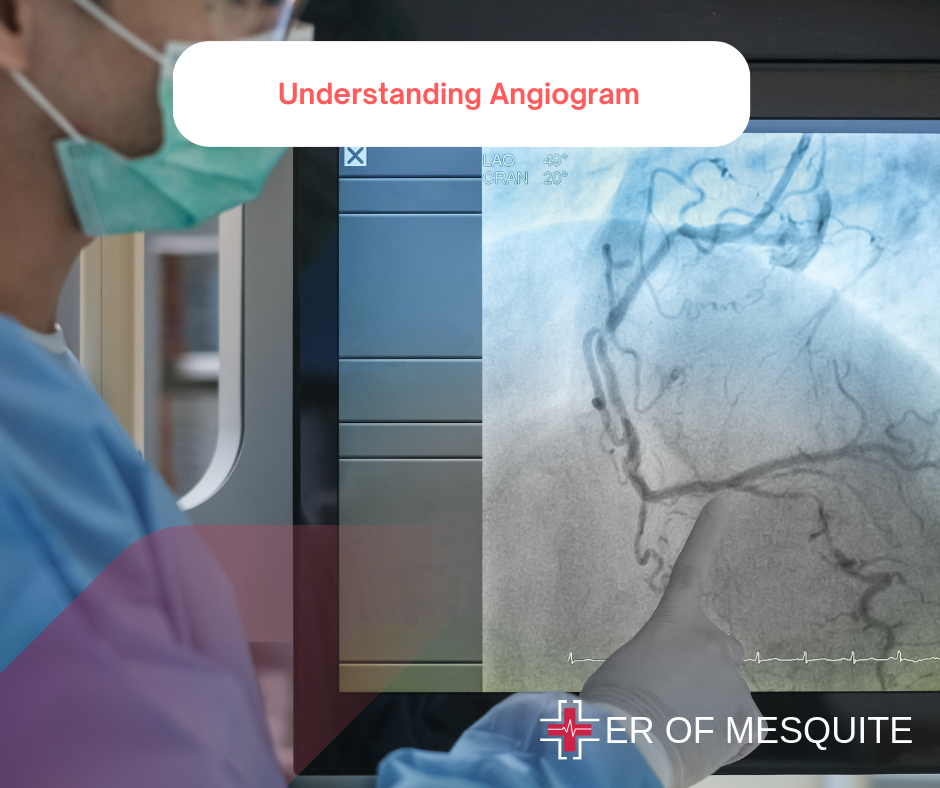
An Angiogram, specifically a Coronary Angiogram, is an invasive procedure used to visualize the coronary arteries and detect any blockages or abnormalities that could affect blood flow to the heart. This technique involves the use of a catheter, contrast dye, and X-ray imaging to provide a detailed view of the blood vessels.
Angiogram Procedure typically includes:
- Preparation: Just like a CT scan, your doctor may recommend fasting for a few hours before the surgery. Notify your doctor of any allergies or medications being taken, as these can impact the treatment.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or arm. This thin, flexible tube is carefully guided to the coronary arteries using X-ray imaging.
- Contrast Dye Injection: Once the catheter is in place, a radiopaque contrast dye is injected through it into the bloodstream. This dye highlights the arteries and blood flow on the X-ray images.
- Imaging: X-ray images are taken to visualize the coronary arteries and detect any blockages or narrowing.
- Post-Procedure: After the imaging, the catheter is removed, and monitoring occurs for a short period. The doctor reviews the images and discusses the findings.
Uses of Coronary Angiograms:
- Diagnosing Coronary Artery Disease: Identifying blockages or narrowing in the coronary arteries.
- Evaluating Heart Function: Assessing how well the heart is functioning and how effectively blood is flowing to it.
- Guiding Treatment: Helping to determine the best course of action, such as angioplasty or stent placement.
The invasive nature of the angiogram allows for more direct and detailed visualization of the blood vessels. However, it also carries risks associated with catheter insertion, such as bleeding or infection.
Cardiac CT Scan vs Angiogram: Key Differences
Cardiac CT Scan vs Angiograms Both are distinct imaging techniques with key differences. Here are the main factors that set these two methods apart:
- Invasiveness: The cardiac CT Scan is non-invasive, while angiograms require catheter insertion into a blood vessel.
- Imaging Detail: Angiogram offers a more direct view of the coronary arteries and is particularly useful for diagnosing significant blockages or narrowing. The cardiac CT scan provides high-resolution images for evaluating the overall coronary anatomy.
- Procedure Time: A cardiac CT scan typically takes less than 30 minutes. Angiograms may take longer due to the catheter insertion, imaging, and post-procedure monitoring.
- Risks: Both procedures involve exposure to contrast dye and X-rays, but the Angiogram carries additional risks related to catheter insertion, such as bleeding, infection, or damage to the blood vessels.
- Preparation and Recovery: Cardiac CT Scans typically require less preparation and recovery time compared to Angiograms. After a CT Scan, you can usually return to your normal activities right away. In contrast, recovery from an Angiogram might involve a short period of observation and possible restrictions on activities.
Choosing the Right Imaging Method
The choice between a Cardiac CT Scan vs Angiogram both depends on factors like the patient’s health status, specific medical condition, and the urgency of the diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will recommend the most appropriate option based on your individual case.
- Cardiac CT Scans are often preferred for initial evaluations, particularly in cases where non-invasive imaging is sufficient to diagnose or rule out heart conditions. They are useful for detecting coronary artery disease, assessing heart valves, and identifying congenital defects.
- Angiograms are typically reserved for cases where more detailed, invasive imaging is needed, such as when significant blockages are suspected or when precise treatment planning is required. They are often used in emergency situations or for patients who require procedures like angioplasty or stent placement.
Key Takeaway
Cardiac CT Scan vs Angiograms both play crucial roles in heart imaging and diagnostics. Each method has unique advantages, and the choice between them should be guided by your healthcare provider based on your specific health needs and conditions.
At ER of Mesquite, we are committed to providing exceptional, timely care for all your urgent medical needs. Our state-of-the-art facility provides advanced imaging services in Mesquite Tx for precise and accurate diagnoses of various heart conditions.
Schedule Your Heart Health Consultation
FAQs
Can CT scan detect heart blockage?
Yes, a CT scan can detect heart blockage by providing detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify any obstructions.
How accurate is a cardiac CT scan?
A cardiac CT scan is highly accurate in detecting coronary artery disease. It offers detailed images of the coronary arteries to identify blockages or abnormalities.
Can a blockage be missed on a CT scan?
A blockage can occasionally be missed on a CT scan, especially if it’s very small or located in a challenging area to image.